Nx Uf

Lh Nnf Emfkf Kzkltgfy Dl Gb s S

Genuine Nos Rubycon Black Gate Capacitors 2 X 0 47uf 50v Nx Hiq Private Sale 80 00 Picclick Uk

Help To Understand The Ring Of Polynomials Terminology In N Indeterminates Mathematics Stack Exchange
Cosmological Vlasov Poisson Simulations Of Structure Formation With Relic Neutrinos Nonlinear Clustering And The Neutrino Mass Iopscience

Find The Derivative Of Sin N X
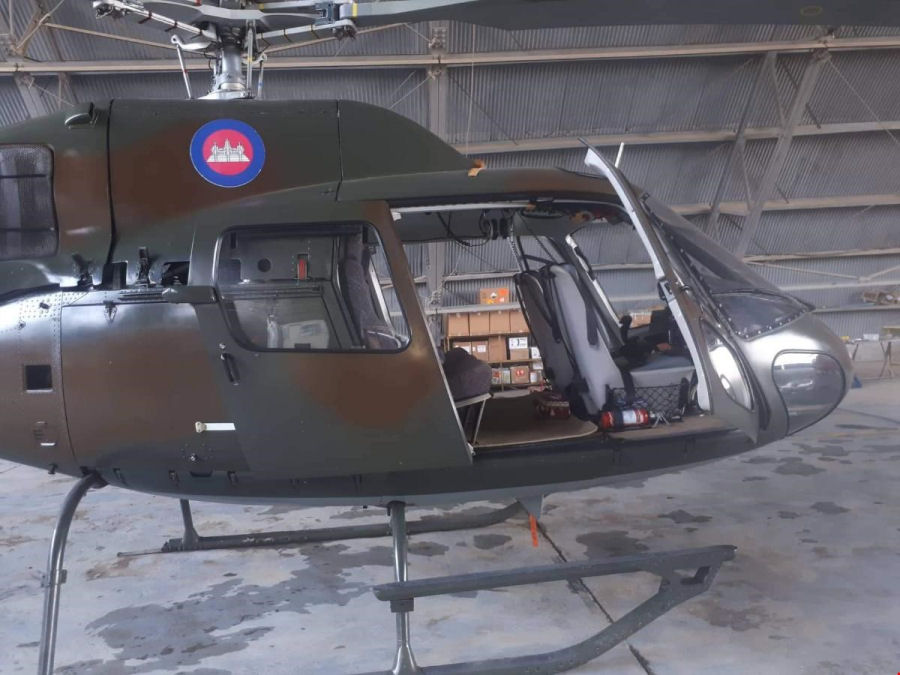

Xu 018 F Ohkh Eurocopter As355n Ecureuil 2 C N 5622
Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of Nevada, Reno Reno, NV 557 Email Qipingataolcom Website wwwcseunredu/~yanq I came to the US.

Nx uf. N x L an t L an B L an t L an u xt A π π π π π Set t = 0 and equate it with g(x) ( ,0) sin 1 g x L n x L an u x B n t =∑ n = ∞ = π π We see that g(x) needs also be a Fourier sine series Expand it into its odd periodic extension (period 2 L), if necessary Once g(x) is written into a sine series, the previous equation becomes. But since f is given by an in nite sum, we look for a candidate solution in the form of an in nite linear combination u(x;y) = X1 n=1 b nsinh nˇ L (x L) sin nˇ L y By. N) X n P(A n) (iii) For every nwe can write A n as the disjoint union A n= (A nnA n1) (A n1 nA n2) (\ nA n);.
It is o b vio u s th a t th e p o lyn o m ia ls F n (x) are o b ta in e d by le ttin g H Q (X ) = 0, Hi(x)= 7, whil e th e Lucas p o lyn o m ia ls L n (x) are o b ta in e d by le ttin g HQ(X) = 2 and Hf(x)= 1 In fa ct, it can be e sta b lish e. U(f;D n) = 1 4 1 2n 1 4n2 As n!1we have L(f;D n) !1 4 and also U(f;D n) !1 4 From this it follows that fis integrable on 0;1 and that Z 1 0 x3dx= 1 4;. Let us start with an example Here we have the function f(x) = 2x3, written as a flow diagram The Inverse Function goes the other way So the inverse of 2x3 is (y3)/2.
4,247 Followers, 80 Following, 930 Posts See Instagram photos and videos from L U F I A N X Y (@lufianxy_official). Unsafe int NXOpenUFUFAssemAskAllPartOccChildren (NXOpen part_occur, out NXOpen child_part_occs. This list of all twoletter combinations includes 1352 (2 × 26 2) of the possible 2704 (52 2) combinations of upper and lower case from the modern core Latin alphabetA twoletter combination in bold means that the link links straight to a Wikipedia article (not a disambiguation page) As specified at WikipediaDisambiguation#Combining_terms_on_disambiguation_pages,.
Note The notation N = N(x,ε) means that the natural number N depends on the choice of x and ε 3 I Uniform convergence Definition Let D be a subset of R and let {f n} be a sequence of real valued functions defined on D Then {f n} converges uniformly to f if given any ε > 0, there exists a natural number N = N(ε) such that f n(x)−f(x) < ε for every n > N and for every x in D. 14/12/ · u= f in ;. If F(u)= f(x,y,z) be a homogeneous function of degree n in x,y,z, then x ∂ x ∂ u y ∂ y ∂ u z ∂ z ∂ u = A F (u) F (u) B n F (u) C nu D None of these Answer Correct option is B n F (u) A function f is called homogeneous of degree n, then it will satisfy the equationf (t x, t y, t z) = t n f (x, y, z) f (x, y, z) = F (u) Let, p = t x q = t y r = t z Therefore, d t d.
N(x) exists for every x ∈ X, then f = g 3 = g 4, so f is measurable Let (f n) n=1,2, be a sequence of functions from a nonempty set X to IR We say that the sequence converges uniformly to a function f X → IR if, for any ε > 0, there exists a positive integer N such that f n(x) − f(x) < ε whenever n ≥ N and x ∈ X 4 Let X be a nonempty set The characteristic function of a. Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, history. Therefore lim k!1(U(f n;P k) L(f n;P k)) = 0However, f n converges pointwise on 0;1 to f= ˜ Q, which is not Riemann integrable on 0;1 Problem 15 Verify the assertions in the last Remark of this section Solution Yup, the Remark is true Problem 16 Let fbe a nonnegative bounded measurable function on a set of nite measure.
It's simple to see that the pointwise limit of $(f_n)_n$ is the zero function but $$f_n_\infty\ge f_n\left(\frac 1 n\right)=\left(1\frac 1 n\right)^n\to e^{1}\ne0$$ so the convergence isn't uniform on the interval $0,1$. 4 Solution For each n2N, h n is clearly integrable on 0;1 and jh n(x)j 1=2n for all x Thus the series P 1 n=1 h n(x) converges uniformly and H is integrable by Theorem 744 We have Z 1 0 h n= 1 2 n 1 1 2 n 1 2 1 22 Thus Z 1 0 H= X1 n=1 Z 1 0 h n= 1 n=1 1 2n X1 n=1 1 4n = 1 1 3 = 2 3;. 2 Remember that we proved this in the rst lecture?.
φ(U∩f−1(V)) φ −1 U∩f−1(V) f V ψ C is holomorphic It is worthwhile to mention that this notion will not change if one replace the atlases on Xand on Y with equivalent (other) atlases The following special cases are of interest 221 Holomorphic functions on a RS Let X be a RS A holomorphic map f X → C is called a. U f O X Ȃ̂ Ǝv ܂ A L ` ͍ 荂 L Ɏ B ܂ X v t H N ₷ A ˂ o ␅ َq ɂ B ` J b g L L P A G ߂̕ ̍ʂ A N ₩ o Ă ܂ B C M X WEBB CORBETT ɂ A B e W ̃J b g N X ^ O X B2 q1 g ł̂ Љ ł B e ʂ͂ Ŗ 180cc B. Inverse Functions An inverse function goes the other way!.
4 See Proposition 1314 on page 15 of the text to obtain P(A n) = P(A nnA n1) P(A n1 nA n2) P(\ nA n) This shows that P(A n) P(\ nA n) is the tail of a convergent. (see the previous section on Grover’s algorithm)To understand how the DeutschJozsa algorithm works, let us first consider a typical interference experiment a particle that behaves like a wave, such as a photon, can travel from the source to an array of detectors by following two or more paths simultaneously. For the first time since the dawn of the suburbs, America seems ready to begin realizing its urbanist mistakes, and transform policy to encourage healthy nei.
U f yy u)du (f xx v f yy v)dv = f udu f vdv If we write this out in long form, we have @f @u = @f @x @x @u @f @y @y @u and @f @v = @f @x @x @v @f @y @y @v Example 112 Suppose that w= f(x;y) and we change from Cartesian to polar coordinates, x= rcos y= rsin We have @x @r = cos @x @ = rsin @y @r = sin @x @ = rcos So f r= cos f x sin f y f = rsin f x rcos f y 2 Created. Y*u(f) = f fdGy*, /ec(n,x), ^r, JQ see 3, 4, 8, 9 for more details The measure G is called the representing measure of U Also, for a linear and continuous operator U C(fž, X) » F, we can associate in a natural way two linear and continuous operators U* C(Si) L(X,Y) and f/# X > L (C (fi) , F) defined by (U&ip) (x) = U ((p 0 x) and {U#x) (. Ig So if d(x;a) < , then jf i(x) f i(a)j< p 2=nfor all i, and so d(h(x);h(a)) = v u u t.
5 (a) Determine the Taylor polynomial Pn(x) of degree n centered at 0 for the function ex (b) Give an expression for the remainder Rn(x) in Taylor’s theorem such that ex = P n(x)Rn(x) (c) Prove that ex ≥ 1x for all x ∈ R, with equality if and only if x = 0 (d) Prove that eˇ > πe Hint Make a good choice of x in (c) Solution. N(x)) de nes a continuous function from Rm into Rn We prove this generalized statement, which in particular proves the case m= 1 and n= 2 Let a2Rmand >0 Since each f iis continuous for i= 1;;n, by De nition 401 there exists isuch that if d(x;a) < i, then jf i(x) f i(a)j< p 2=n Let = minfd 1;;. Intuitively, a function is a process that associates each element of a set X, to a single element of a set Y Formally, a function f from a set X to a set Y is defined by a set G of ordered pairs (x, y) such that x ∈ X, y ∈ Y, and every element of X is the first component of exactly one ordered pair in G In other words, for every x in X, there is exactly one element y such that the.
Savings Bank Card Cheque Coins Spend Tick the box when you’ve found each word!. Let u= f(x,y,z), v= g(x,y,z) and ϕ(u,v) = 0 We shall eliminate ϕ and form a differential equation Example 3 From the equation z = f(3xy) g(3xy) form a PDE by eliminating arbitrary function Solution Differentiating wrto x,y partially respectively we get 3 '( 3 ) 3 '( 3 ) f '( 3x y ) g '( 3x y ) y z f x y g x y and q x z p w w w w 9 ''( 3 ) 9 ''( 3 ) ''( 3 ) ''( 3 ) 2 2 2 2 f x y g x y. 627 Followers, 1,005 Following, 5 Posts See Instagram photos and videos from M c M u f f i n x 3 3 ♡ (@mcmuffinx33).
N x w o f u a r p a m l o s o o o o jokes what always comes at the end of thanksgiving?. @u @n = gon ;. (because he had the drumsticks) e m b l k f a s b u r r u f e b u n e u o r n a q s d kind created date 11/8/16 pm.
01/02/21 · In this section we will be looking at Integration by Parts Of all the techniques we’ll be looking at in this class this is the technique that students are most likely to run into down the road in other classes We also give a derivation of the integration by parts formula. 3 I just knew that Exercise 3 would come in handy!. Step 3 If U f(Y) cg(Y) set X= Y Otherwise, go back to Step 1 Assuming that successively generated random variables are independent, show that (a) Xhas density function f (b) the number of iterations of the algorithm needed to generate Xis a geometric random variable with mean c.
There is a compatible condition for fand g (7) Z fdx= Z udx= Z @ @u @n dS= Z @ gdS A natural approximation to the normal derivative is a one sided difference, for example @u @n (x1;yj) = u1;j u2;j h O(h) But this is only a first order approximation To treat Neumann boundary condition more accurately, we introduce the ghost points outside of the. U = f(r), where r = p (x2y2z2) U is a function of r alone so df/dr exists As U = f(x,y,z) also, ∂f ∂x = df dr ∂r ∂x ∂f ∂y = df dr ∂r ∂y ∂f ∂z = df dr ∂r ∂z ⇒ ∇∇U = ∂f ∂x ˆı ∂f ∂y ˆ ∂f ∂z ˆk = df dr ∂r ∂x ˆı ∂r ∂y ˆ ∂r ∂z ˆk But r = p x2y2z2, so ∂r/∂x = x/r and similarly for y,z ⇒. P a a b ŁA ҃e r f 扻 i1999 N N X } X E C u ɕ f j @Jane Prowse ē A V A r { ł 014 N ɏo ł Ă ̂ނ (The Great Blue Yonder) @ l 05 (01) 04 N11 ɋ W j A ł s ꂽ ֘A T C g Pan Macmillan T.
S X A U F Z C D Y Y E A D V O T H R H R E P V T O F E A W D I P C I U R Q C R K K J N O N X U S G C D N E P S G E L O H T T A J S B S I E E B F O B R B N W X D G N H A E S S V C Q L K H O M I V I H R Can you find all of the words relating to money in the wordsearch?. 09/04/11 · It seems to me like you made a mistake Since the both f(x) and its derivative are raised to the n power, you can't use usubstitution to get rid of the f '(x). Where we used again Theorem 744 and Theorem 271 (i), (ii).
N−x ways of choosing nx of the N M males Therefore, there are M x × N −M n−x waysof choosing x femalesand nx males Because there are N n waysof choosing n of the N elementsin theset, and because we will assumethatthey all are equally likely the probability of x femalesin a sample of sizen is given by pX(x)=P(X = x)= M x N −M n−x N n for x=0, 1, 2, 3,···,n and x ≤ M,. Therefore, in an upper Riemann sum U(f;P) we evaluate f at the right endpoints and in a lower Riemann sum L(f;P), we evaluate f at the left endpoints • Let P be the partition of 0,1 into n intervals of equal length 1/n with endpoints xk = k/n, where k = 0,1,,n • For this partition, U(f;P) = 1 n k=1 k/n 1(k/n)2 = k=1 k n2 k2, L(f;P) = 1 n k=1 (k −1)/n 1((k − 1)/n) 2. N(x;y) = 1 sinh(nˇ) sinh nˇ L (x L) sin nˇ L y In the general case, we rst proceed formally Observe that nite linear combinations of the u n given by (18) are still harmonic and 0 on the three sides of the square;.
A priori bounds for solutions of the Dirichlet problem for ∆ λ 2 n( x) u = f( x, λ) on an exterior domain. With n x and n y = 1,2,3, Show that this wavefunction is normalized 10 Using the same wavefunction, Ψ (x,y), given in exercise 9 show that the expectation value of p x vanishes 11 Calculate the expectation value of the x 2 operator for the first two states of the harmonic oscillator Use the v=0 and v=1 harmonic oscillator wavefunctions given below which are normalized such. Money Matters Created Date 9/15/16.
As required (2)Suppose that g(x) is a continuous function on an interval a;b such that g(x) >0 for all x Show that Z b a g(x)dx>0 Solution Since g(x) 6= 0 on a;b the function 1 g is de ned and continuous on a;b Hence there. ∂2u F = (ρΔx) (2) ∂t2 where ρ is the linear density of the string (ML−1) and Δx is the length of the segment The force comes from the tension in the string only we ignore any external forces such as gravity The horizontal tension is constant, and hence it is the vertical tension that moves the string vertically (obvious) Balancing the forces in the horizontal direction gives T. Definition In this article, the field of scalars denoted 𝔽 is either the field of real numbers or the field of complex numbers Formally, an inner product space is a vector space V over the field 𝔽 together with a map , → called an inner product that satisfies the following conditions (1), (2), and (3) for all vectors x, y, z ∈ V and all scalars a ∈ 𝔽.
N = x for all n > N Indeed, suppose that (x n) converges to x but that for everyN > 0 there is n > N such that x n, x This implies that there is a subsequence (x n k) of (x n)with all x n k, x The open set U = X \{x n k k = 1,2,···} contains x and witnesses the failure of (x n) to converge to x ¶ 6 Let X be the set of positive. " of a;b such that U(f;P ") L(f;P ") < " The sequence (f n) converges uniformly to f, so there exists N such that, if n > N, then jf n(x) f(x)j< " 4(b a) for all x 2a;b By hypothesis f N1 is integrable, so there exists a partition P " = fx 0;x 1;;x kgof a;b such that U(f N1;P ") L(f N1;P ") = Xk i=1 (M i;f N1 m i;f N1) x i < " 2 (1) Now, N 1 > N, so jf N1(x) f(x)j< " 4(b a. (the letter why was the turkey the drummer in the band?.

How Can I Locate Items In The Same Height Which Is Located In Different Columns Tex Latex Stack Exchange

I Just Leave It Here

2 An Integral For A First Order Ordinary Differen Chegg Com
Sm U 35 High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy

Ppt Optimal Control Of Systems Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
Continuous Probability Distributions Ppt Video Online Download

C6fwg3oifylscm
Sample Problem Set Solutions

Diffusion Equations Springerlink

Order Statistics Expected Value Of Range E X N X 1 Cross Validated

Buy Nx Smd Tantalum Capacitor 6 V 470 Uf 7343 6 3 V Tantalum Capacitors 477 D Type Thin Seed In Cheap Price On Alibaba Com
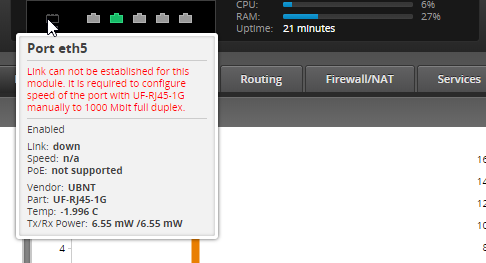
Edgerouter X Sfp With Uf Rj45 1g Module Ubiquiti Community

The Derivative Of Log X Sin X Sins Product Rule Calculus

Answered Sets Worksheet 1 1 State Whether Each Bartleby
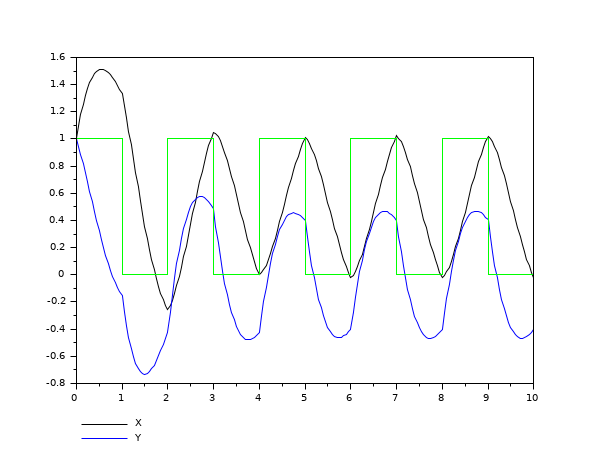
Odedc Discrete Continuous Ode Solver
Installing Nx Templates In Teamcenter Integration For Nx

Wave Equations Springerlink

4 X Suflex 9500pf 9 5n 0 0095uf 350v Dc 2 Polystyrene Capacitor Ebay

Diffusion Equations Springerlink

Misc 30 Find Derivative X Sinn X Chapter 13 Class 11

Solved Solve The Following Problems Ut X T Uxx X T Chegg Com

Section 2 3 Suppose X Is A Discrete Type Random Variable With Outcome Space S And P M F F X The Mean Of X Is The Variance Of X Is The Standard Deviation Ppt Download

Chapter 3 Generating Uniform Random Variables Generating Uniform

Final Normalized Transverse Emittance F N X And Energy Spread S F U Download Scientific Diagram
Feedback Linearization Wikipedia

An Introduction To Partial Differential Equation With Matlab Pages 151 0 Flip Pdf Download Fliphtml5

Ma100 Calculus Summary Mathematical Methods Studocu

F Zero Nx For Switch W Retro Manual Fzero

Pdf Dynamic Euler Bernoulli Beam Equation Classification And Reductions

Numerical Solution Of Elliptic Partial Differential Equation Programmer Sought

Ttoba S Art Blog Undertale Cute Undertale Fanart Undertale

Yi Zhuang You Ucsd 08

Fourier Transform Cs Prof Bebis Sections 4

Filter Networkx Graph To List All Edges Coming From A Nodes With Specific Attributes Stack Overflow
3 4 Fourier Transform Theoretical Physics Reference 0 5 Documentation

Diffusion Equations Springerlink
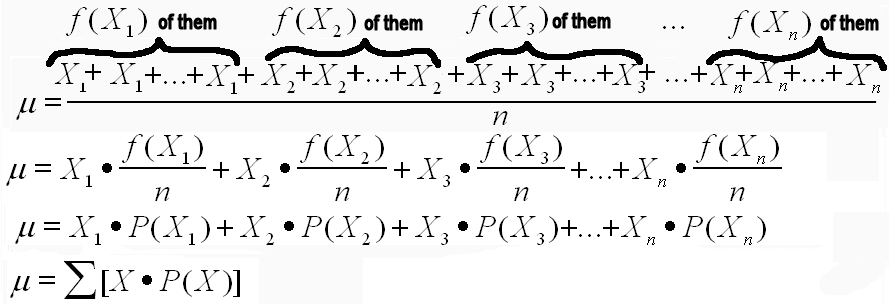
Basic Probability And Counting Problems

Solved 10 Points Show That The Functions U N X T 1 Chegg Com

Wave Equations Springerlink

Answered Consider A Thin Plate Of Length L And Bartleby

A Regular Surface S Is Orientable Iff There Exists A Differentiable Field Of Unit Normal Vectors On S Mathematics Stack Exchange

Observation Of Weyl Nodes And Fermi Arcs In Tantalum Phosphide Nature Communications X Mol

Wave Equations Springerlink

Generate R V Monte Carlo

Solved Q2 Let X1 X2 X Are Uniform Random Variabl Chegg Com

Functions Of Random Variables 2 Method Of Distribution Functions Online Presentation
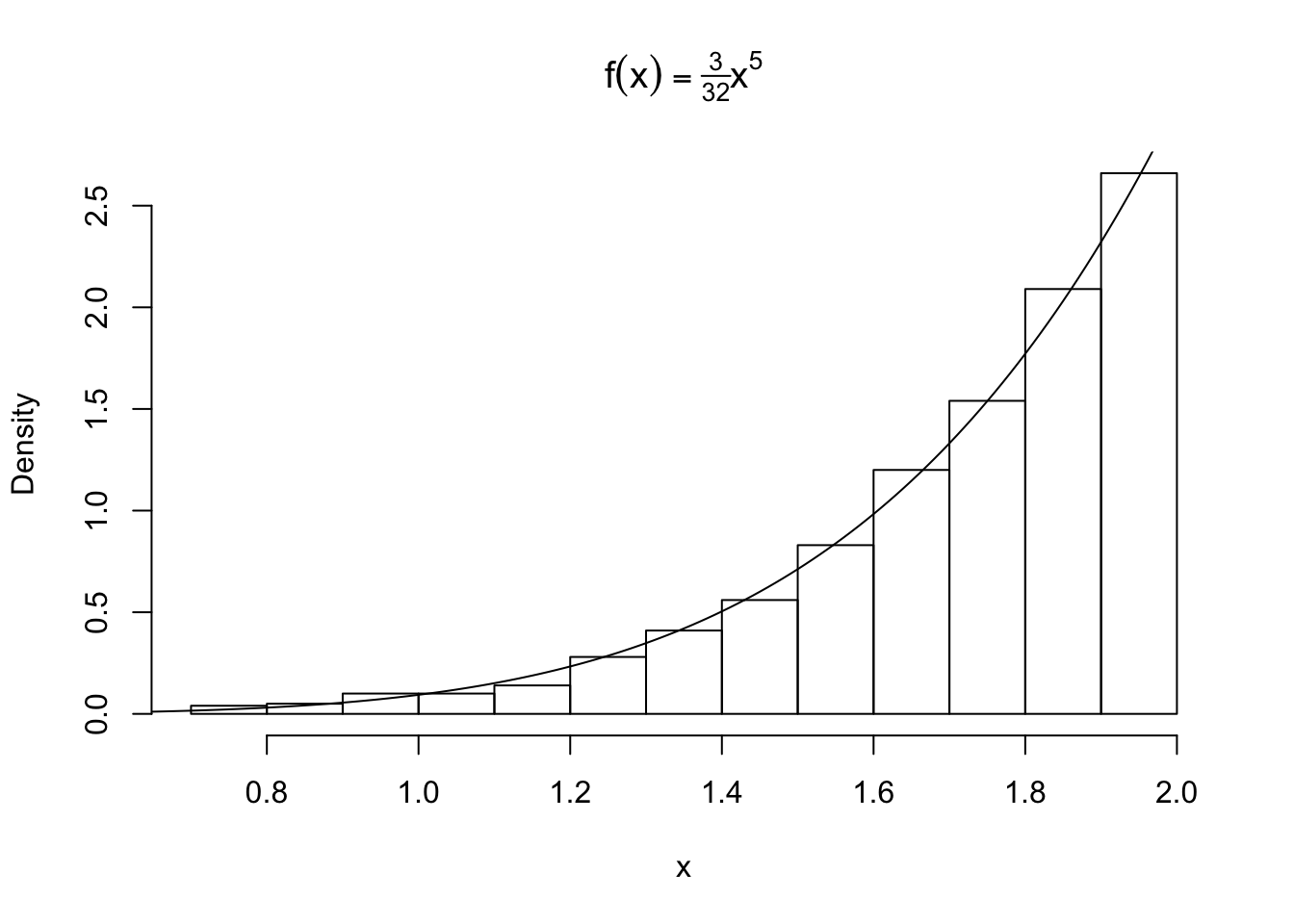
Simulation

Use The General Equation U N Xt E 2 N 2 Pi 2 Tl 2 Sinnpix Now We Can Plug Our U Course Hero
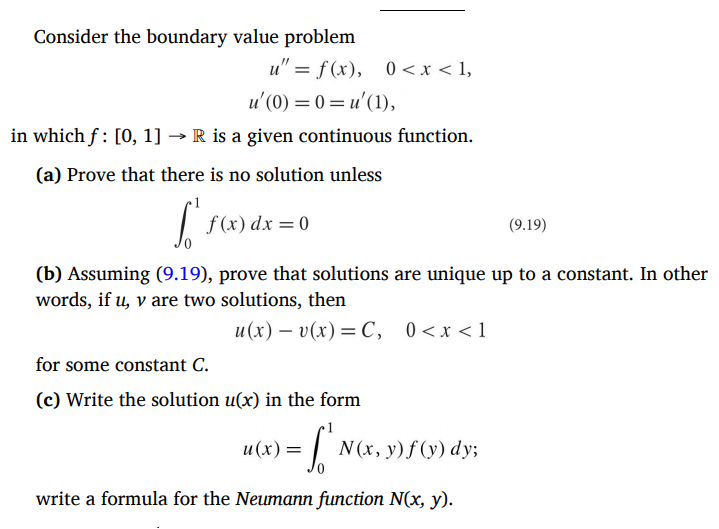
Consider The Boundary Value Problem U F X U Chegg Com
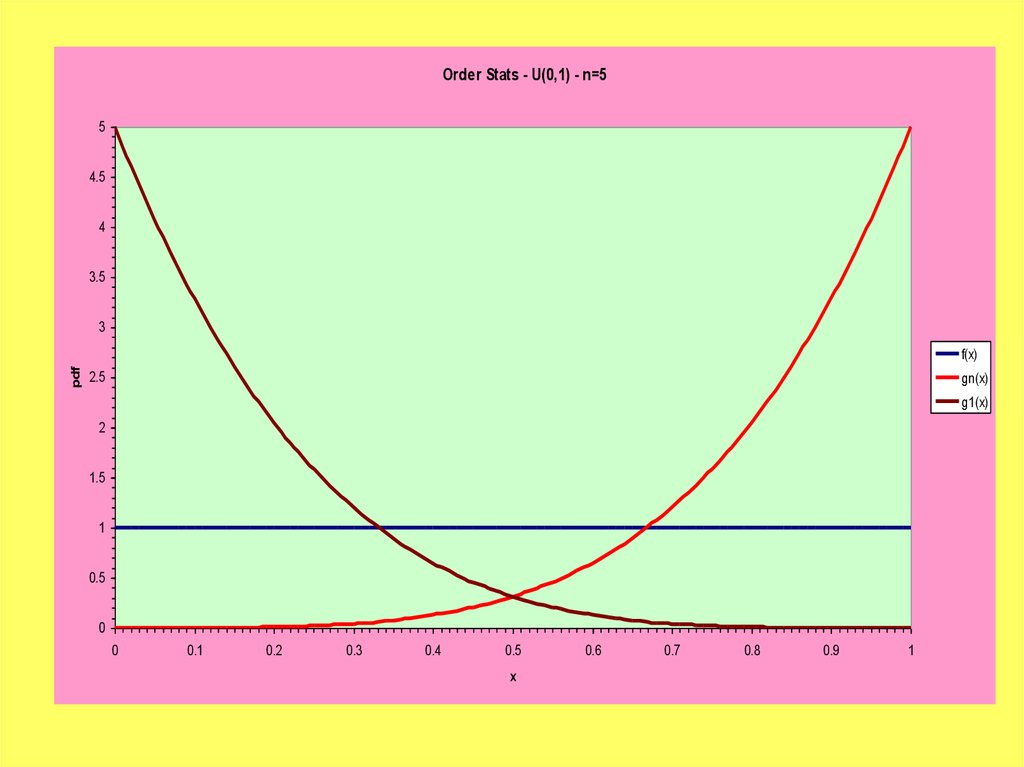
Functions Of Random Variables 2 Method Of Distribution Functions Online Presentation

Graph Of F R S N X Y U V N 10 U 0 3 V 0 6 R 3 S 2 Download Scientific Diagram

A Block By Block Method With Romberg Quadrature For The System Of Urysohn Type Volterra Integral Equations

Diffusion Equations Springerlink

Fluids Free Full Text Cfd Julia A Learning Module Structuring An Introductory Course On Computational Fluid Dynamics Html

General F Theory Models With Su 3 X Su 2 X U 1 Z 6 Symmetry Andrew Turner Youtube

Diffusion Equations Springerlink
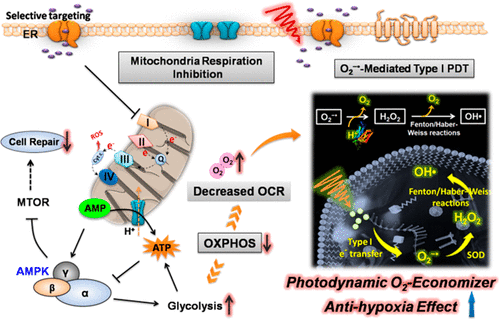
En Journal Publications 精细化工彭孝军课题组

1 Vytah

Continuous Probability Distributions Ppt Video Online Download

Black Gate Hi Q Nx 0 1uf 50v Capacitors Electronics Others On Carousell

Jacobians New

Numerical Solution Of Elliptic Partial Differential Equation Programmer Sought

Let S Code The Roots Of Functional Programming Lambda Calculus Implemented In Typescript By Enrico Piccinin Hackernoon Com Medium



