Fxe U Z
What Is The Analytic Function Math F Z Math In Terms Of Math Z Math Whose Real Part Is Math E X X Sin Y Y Cos Y Math Quora

Ballfun Chebfun

Superficie Nello Spazio Loro Area Formule Della Divergenza

Solved Find The Differentials Of The Following Functions Chegg Com

If U Ex X Cosy Y Siny Then The Analytic Aspirebuzz

Answered 9 M A Y Z Xyz Xyz P 2 1 1 U Bartleby
6041/6431 Spring 08 Quiz 2 Wednesday, April 16, 730 930 PM SOLUTIONS Name Recitation Instructor TA Question Part.

Fxe u z. E b h t F X p 950 @ P iSFP950DBRSST t F X E g X X g g _ N u E iJAN R h j ̃y W ł B i 1 `2 c Ɠ ȓ ɔ ܂ i y j j B DCM I C ͏Z ܂ X ^ C ̃t F X E g X w z Z ^ ʔ̃T C g ł BDCM I C ł̓K f j O E p i ͂ ߂Ƃ A 34 _ ̏ i 舵 Ă ܂ B z Z ^ ʔ DCM I C ł̂ y ݂ B. If this was the case, solving e^ {Ax}\left (xE\right)^2=D Only if (x2 Bx C) = (x E)2 is a perfect square, that is to say if B2 = 4C, E = 21 B you would have analytical solutions in terms of Lambert function If this was the case, solving eAx(x E)2 = D. M11 Cálculo II Derivadas parciais Regra da cadeia Regra da cadeia Selecione os exercícios por Dificuldade Fácil Médio Difícil Categoria Exercício Contextualizado Prática da Técnica Prática de Conceitos Demonstrações Problemas Complexos Outros.
{eq}f(x, y, z) = xe^{2yz}, P(3, 0, 2), u = {/eq} Find the gradient of {eq}f {/eq} Evaluate the gradient at the point {eq}P {/eq}. 4 U m = 3 Ax 2 R3 0 5 Ax = 2 1 1 3 § ± » Q§ =) C(A) = R3 64 7 ¨ r < m 1 5 ¦ V W4 Q ¨ X X ³ 8 ³ >Y m = 3 r ¡§ ° m = 3 = n = 1 r = n = 2x;Z³§ N(A) = f0g > » Ax = 2 0 1 3 1 ¨ Q± » Q§x \U 8 ³ ¦ » § » 3 Q±³» 6 ³ Q§V 4 8 0 5 7 Ax = 0;. \mathbb{Z} \emptyset \vee \wedge \neg \oplus \cap \cup \square^{c} \subset \subsete \superset \supersete.
Of u = g(x), then Z b a f(g(x))g0(x)dx = Z g(b) g(a) f(u)du Example Calculate R e 1 lnx x dx Solution We let u = lnx because its differential du = dx x occurs in the integral When x = 1, u = ln1 = 0;. Z A p X(x)dx= Z A p(x)dx and p X(x) = p(x) = F0(x) The following are all equivalent X˘P;. Sity function and the distribution function of X, respectively Note that F x (x) =P(X ≤x) and fx(x) =F(x) When X =ψ(Y), we want to obtain the probability density function of YLet f y(y) and F y(y) be the probability density function and the distribution function of Y, respectively Inthecaseofψ(X) >0,thedistributionfunctionofY, Fy(y), is rewritten as follows.
In mathematics, an exponential function is a function of the form f ( x ) = a b x, {\displaystyle f(x)=ab^{x},} where b is a positive real number, and the argument x occurs as an exponent For real numbers c and d, a function of the form f ( x ) = a b c x d {\displaystyle f(x)=ab^{cxd}} is also an exponential function, since it can be rewritten as a b c x d = ( a b d ) ( b c ) x {\displaystyle. Tion as a complex function f(z) that satisfies the following defining properties 1 f(z) is entire, 2 f′(z) = f(z), 3 f(x) = ex, x is real Let f(z) = u(x,y) iv(x,y), z = x iy From property (1), u and v satisfy the CauchyRiemann relations Combining (1) and (2) ux ivx = vy − iuy = u iv First, we observe that ux = u and vx. V ɂăt F X e B o J ×\ ł B i09/07 j 09/03 09 ^ C C J g Ղ ɂĊJ Â ܂ B i09 j.
Taylor Series A Taylor Series is an expansion of some function into an infinite sum of terms, where each term has a larger exponent like x, x 2, x 3, etc. Math 311 Spring 14 Solutions to Assignment # 4 Completion Date Friday May 16, 14 Question 1 p 77, #1 (a) Apply the theorem in Sec 22 to verify that the function. U z t F X e B o.
Z 1 1 f(x)dx= 1 If we plug in for f(x), we get Z 1 1 Aexp( jxj)dx= 2 Z 1 0 Aexp( x)dx= 2 A exp( x) 0 If 0, this evaluates to in nity, and then there is no way to choose Aso that the area under the pdf is 1 Therefore, it must be that >0 (b)(3 pts) Compute the constant Ain terms of Sketch the pdf Answer Following part (a), we know Z 1 1. V f X E j ƁE u t { H 00 N AIT E j n C ^ ̎d n ߁A w Z u t E X ł WEB T C g ̔ i Ɋւ ƁA C g m x Ĕ u. ̉ t ȁB e } ȁu C E A E g E t E w u v X ^ g B u j O f v A f B Y j A j } ́u n C i v A n C ̓ n i L j ږ ̂ u z z ߁v A o h I W i ȁuLINOTIME v A O q ́u m C s ^ e G v A f t K ȁu v A āu h D E U E t \ t B X e C e b h E t v ł B.
Answer Let X, Y, and Z be indicator random variables such that they are 1 when student 1,2, or 3 gets their homework back respectively and 0 otherwise We also note that the mean of these indicator random variables is 1/3 (in general the mean of an indicator random variable is the. Z ∞ −∞ f(x)eiωxdx (33) such that by replacing (33) in (13) we may express the solution u(x,t) as u(x,t) = Z ∞ −∞ 1 2π Z ∞ −∞ f(x)eiωxdx e−iωxe−kω2tdω (34) which may be written in the equivalent form u(x,t) = 1 2π Z ∞ −∞ f(x) Z ∞ −∞ e−kω2te−iω(x−x)dω dx (35) Notice that g(x) = Z. · For other uses, see Derivative (disambiguation) Operation in calculus The graph of a function, drawn in black, and a tangent line to that function, drawn in red The slope of the tangent line is equal to the derivative of the function at the marked point.
1 5 9 8 7 6 1 5 4 3 1 2 1 ( 0 / & , % $ ' * " ) % $ ) ( ' & % $ # " !. X>0 Note From the pdf of the gamma distribution, if we set = 1 and x= 1 we get f(x) = e We see that the exponential distribution is a special case of the gamma distribution { Find cdf of the exponential distribution { Find the mean of the exponential distribution { Find the variance of the exponential distribution. When x = e, u = lne = 1 Thus Z e 1 lnx x dx = Z 1 0 udu = u2 2 1 0 = 1 2.
Let U and V be independent random variables, each uniformly distributed on 0,1 Determine the mean and variance of the random variable Y = 3U2−2V Second Practice First Midterm Exam 7 Consider the task of giving a 15– minute review lecture on the role of distri. Then we have z u x f x eu x f x e u z a0 a0x a64a64 u u since we are holding u from MATH 237 at University of Waterloo. Free Online Derivative Calculator allows you to solve first order and higher order derivatives, providing information you need to understand derivative concepts.
Solve your math problems using our free math solver with stepbystep solutions Our math solver supports basic math, prealgebra, algebra, trigonometry, calculus and more. 2616 · Explanation Since the derivative of ex is just ex, application of the chain rule to a composite function with ex as the outside function means that d dx (ef(x)) = ef(x) ⋅ f '(x) So, since the power of e is 1 x, we will multiply e1 x by the derivative of 1. Z ˇL ˇL f(x)e inx L dx eint L For purposes of motivation let us abandon periodicity and think of the functions f as di erentiable everywhere, vanishing at t= ˇLand identically zero outside ˇL;ˇL We rewrite this as f(t) = X1 n=1 eint L 1 2ˇL f^(n L).
X˘p Suppose that X ˘P and Y ˘Q We say that X and Y have the same distribution if P(X2A) = Q(Y 2A) for all A In that case we say that Xand Y are equal in distribution and we write X=d Y Lemma 1 X=d Y if and only if F X(t) = F Y(t) for all t 2 Expected Values. 1 1 INTEGRALES DEFINIDAS E IMPROPIAS 1 Hallar el área de la región limitada por la parábola y = x2 − 2x y el eje OX Los cortes de la gráfica de y = x2 − 2x con el eje OX son los valores de x tales que x2 −2x = 0, esto es, x = 0 y x = 2 El área A será. Considere agora a situação z = f(x;y), em que x e y também são funções de duas variáveis s e t, ou seja, x = g(s;t) e y = h(s;t) Neste caso, s e t são as variáveis independentes, x e y são as variáveis intermediárias e z é a variável dependente Regra da Cadeia Caso II Suponha que z = f(x;y) seja uma função diferenciável de x e.
1 > = < 1 ;. Definition 13 For z irrational, we define xz = ez lnx, x > 0 Properties (r and s real numbers) • For x > 0, xr = er lnx • xrs = xr ·xs, xr−s = xr xs, xrs = (xr)s • d dx xr = rxr−1, ⇒ Z xr dx = xr1 r 1 C, for r 6= −1 Example 14 d dx x2 1 3x = d dx e3xln(x21) = e3xln(x21) d dx 3xln(x2 1) = e3xln(x21) 6x2 x2 1 3ln(x2 1) 42 Other Bases. M11 Cálculo II Derivadas parciais Funções implícitas Funções implícitas Selecione os exercícios por Dificuldade Fácil Médio Difícil Categoria Exercício Contextualizado Prática da Técnica Prática de Conceitos Demonstrações Problemas Complexos Outros.
1917 · Now you want to know about the distribution of their difference, namely $Z=XY$ Their mass is $$P(z\ge Z)=P(z\ge XY)=P(z)$$ which is (for $z\le 0$) $$P(z)=\int^\infty_{0}\int^{\infty}_{xz}e^{x}e^{y}\,dy\,dx,$$ as the area of interest is $y\ge xz$ Next, we know that the density $$p(z)=\frac{d}{dz}P(z),$$ is the derivative of the mass. Compute the density of Z from the joint density of X and Y We could then compute the mean of Z using the density of Z Just as in the discrete case there is a shortcut Theorem 1 Let X,Y be jointly continuous random variables with joint density f(x,y) Let g(x,y) R2 → R Define a new random variable by Z = g(X,Y) Then EZ = Z ∞ −∞ Z ∞ −∞. In this *improvised* video, I show that if is a function such that f(xy) = f(x)f(y) and f'(0) exists, then f must either be e^(cx) or the zero function It'.
The series expression for e x looks just like a polynomial We can generalize the idea of a polynomial by allowing an infinite number of terms, just like in the expression for the exponential function An infinite polynomial is called a power series. U=kx so that du = k dx, or (1/k)du = dx Now substitute into the original problem, replacing all forms of x, and getting We now have the following variation of formula 1) 3 The following oftenforgotten, misused, and unpopular rules for exponents will also be helpful and. @ " , ?.
For complex number z z = re iθ = x iy The complex logarithm will be (n = 2,1,0,1,2,) Log z = ln(r) i(θ2nπ) = ln(√(x 2 y 2)) i·arctan(y/x)) Logarithm problems and answers Problem #1 Find x for log 2 (x) log 2 (x3) = 2 Solution Using the product rule log 2 (x∙(x3)) = 2 Changing the logarithm form according to the logarithm definition. H C 擾 AWEB f U C IT Z ~ i ܂ł g ^ Ŏ肪 EastForest i C X g t H X g j ̃T C g ł B. 0 U" X ^ ³ _ ± ± 3 x = 0Q` § a ³ x = h 0 i.
Free Taylor Series calculator Find the Taylor series representation of functions stepbystep. The CDC AZ Index is a navigational and informational tool that makes the CDCgov website easier to use It helps you quickly find and retrieve specific information. @ W F X E u E ւ̈ Ƒ h ɖ f 炵 ` L f ł B X i a قljf 扻 邽 ߂̃l ^ Ղ肠 l Ȃ ̂ł A ꂾ Ɉ { ɂ܂Ƃ߂ ̂͑ ςȍ Ƃ ܂ B Ƃi a Ă A Ȃ Ȃ f ł Ȃ l ^ ͂ ł B A ͎ ׂ ƌ o ˂܂ B.
Z ∞ −∞ x2f X(x)dx = Z 2 1 x2× 2x−2dx = Z 2 1 2dx = h 2x i 2 1 = 2× 2−2 ×1 = 2 Thus Var(X) = E(X 2)−{E(X)} = 2− {2log(2)}2 = 007 Covariance Covariance is a measure of the association or dependence between two random variables X and Y Covariance can be either positive or negative (Variance is always positive). Is the function given below continuous less differentiable at x equals three and they've defined it piecewise and we have some choices continuous not differentiable differentiable not continuous both continuous and differentiable neither continuous nor differentiable now one of these we can knock out right from the getgo it you cannot in order to be differentiable you need to be. Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, history.

Superficie Nello Spazio Loro Area Formule Della Divergenza

1 Vytah
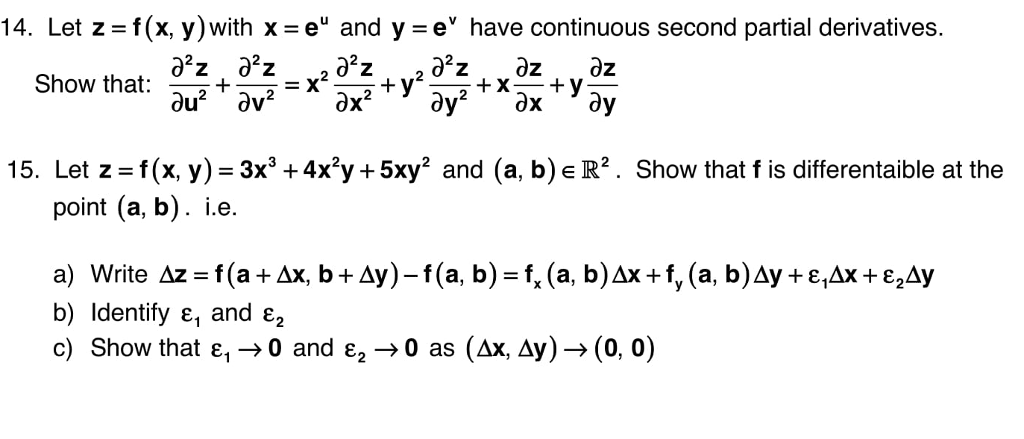
Solved Let Z F X Y With X E U And Y E V Have Con Chegg Com

Let F X Sin Picosx And G X Cos 1pisinx E Two Function Def
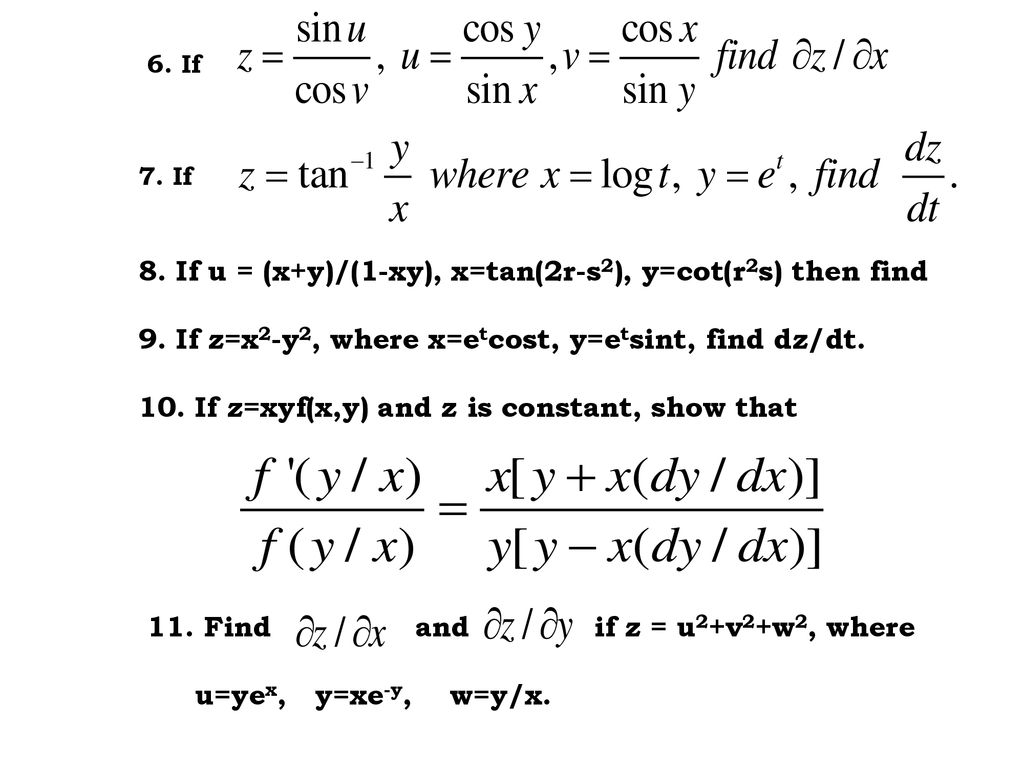
Differentiation Of Composite Function Let Z F X Y Possesses Continuous Partial Derivatives And Let X G T Y H T Possess Continuous Ppt Download

Foglio Di Esercizi N 4 Bis Variabili Aleatorie E Learning

The Derivative Rules For Multivariable Functions Stated Theorem 10 On Page 151 Are Analogous To Derivative Rules From Single Variable Calculus Example Ppt Download

How To Find The Inverse Laplace Transform Of This Mathematics Stack Exchange

List Of Integrals Of Exponential Functions Wikipedia

Answered 53 58 Find All The Second Partial Bartleby

Calculus Problem Sheet Prof Paul Sutcliffe 1 For Each Of The Manualzz

Displacements Of The Slope Isotropic Model Dry Slope A U X B U Download Scientific Diagram

Calculus Assessment 13 Question Sheet Calculus Exercises 13 Please Hand In Your Studocu

Partial Differentiation If Z F X Y X E U E V Y E U V Show әz әu әz әv Xәu әx Yәu әy Youtube
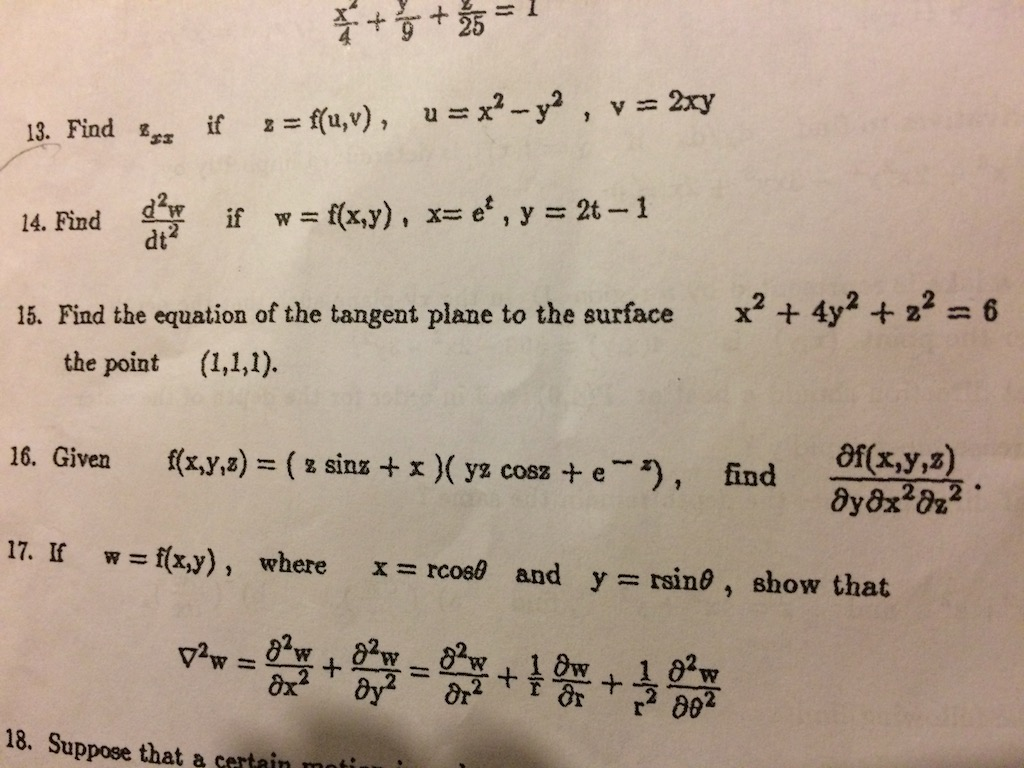
Solved Find Z Xx If Z F U V U X 2 Y 2 V 2xy F Chegg Com

Several Variable Calculus Docsity
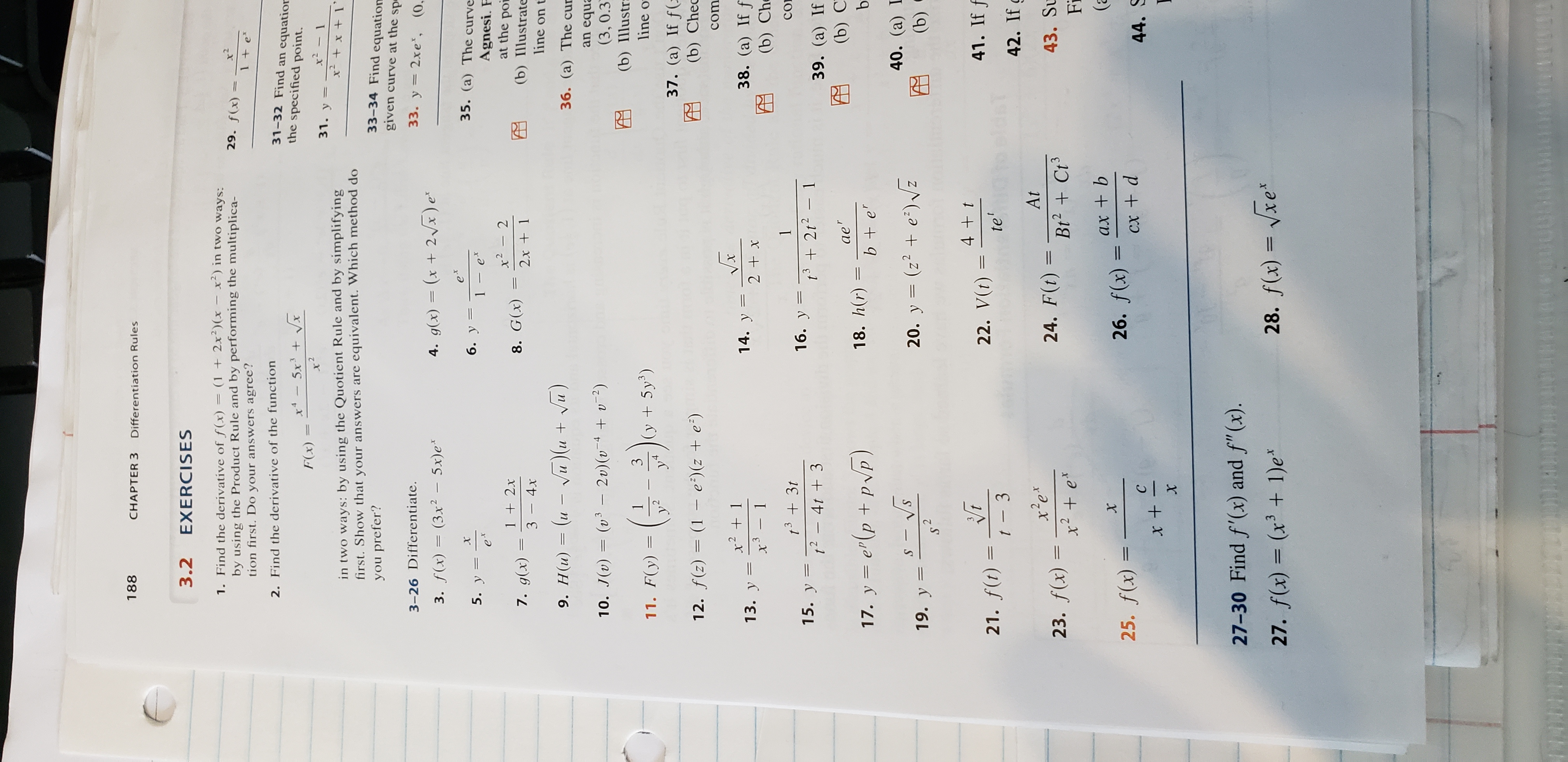
Answered 1 Chapter 3 Differentiation Rules 3 2 Bartleby

Integration By Parts Wikipedia

Solved 18 Determine If F X Y E X Siny Satisfies The Chegg Com

Proximal Mapping Derivation Of The Proximal Operator From The Resolvent Of The Sub Differential Mathematics Stack Exchange

Integration By Parts Wikipedia
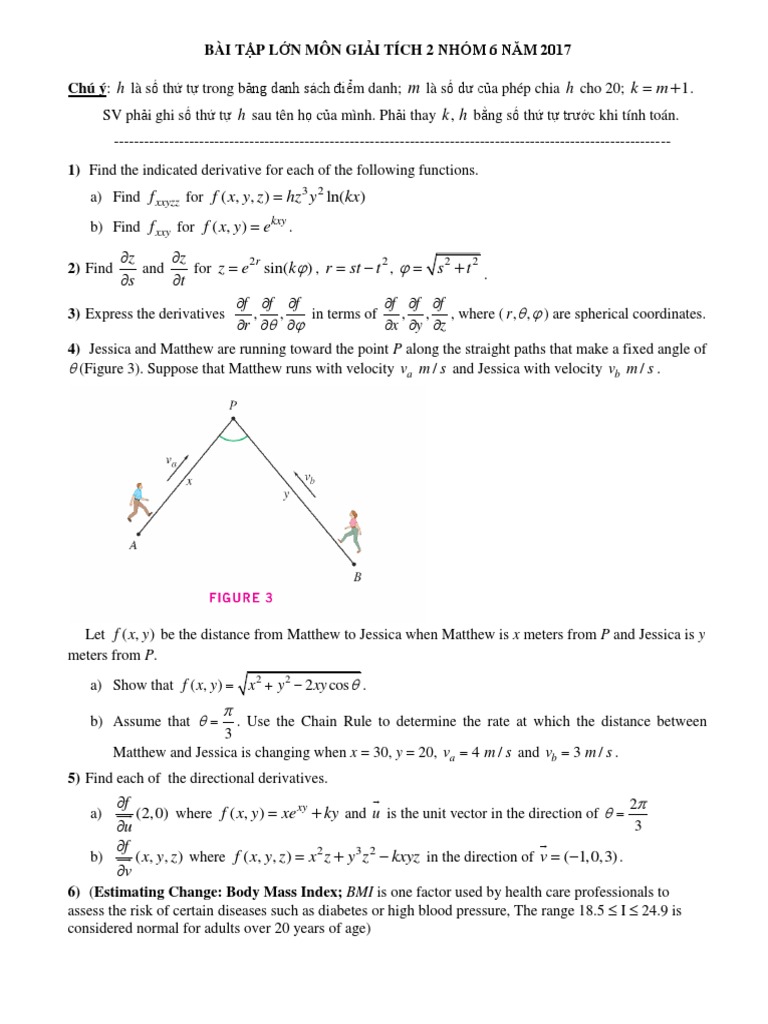
Giai Tich 2 Nam17 Nhom 6 Body Mass Index Maxima And Minima

Teoria Dell Utilita E Decision Process Pdf Download Gratuito
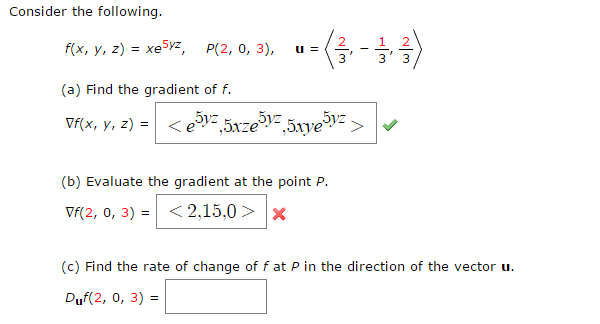
Solved Consider The Following F X Y Z Xe5yz P 2 0 2 U 2 3 2 3 1 3 A Find The Gradient Of F F X Y Z B Evaluate The Gradient Course Hero

Functions Of Several Variables

Week 6

A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z Galvanized Letter Other Home Decor Home Garden

Elementi Di Calcolo Delle Probabilita Pdf Download Gratuito

Find An Analytic Function Of Z X Iy Whose Imaginary Part Is Y Cos Y X Sin Y Expx Holooly Com

Solved 3 Another Version Of The Formula For The Solution Chegg Com
Pdf A Note On Q Calculus

If Z F X Y Where X E U E V Brainly In
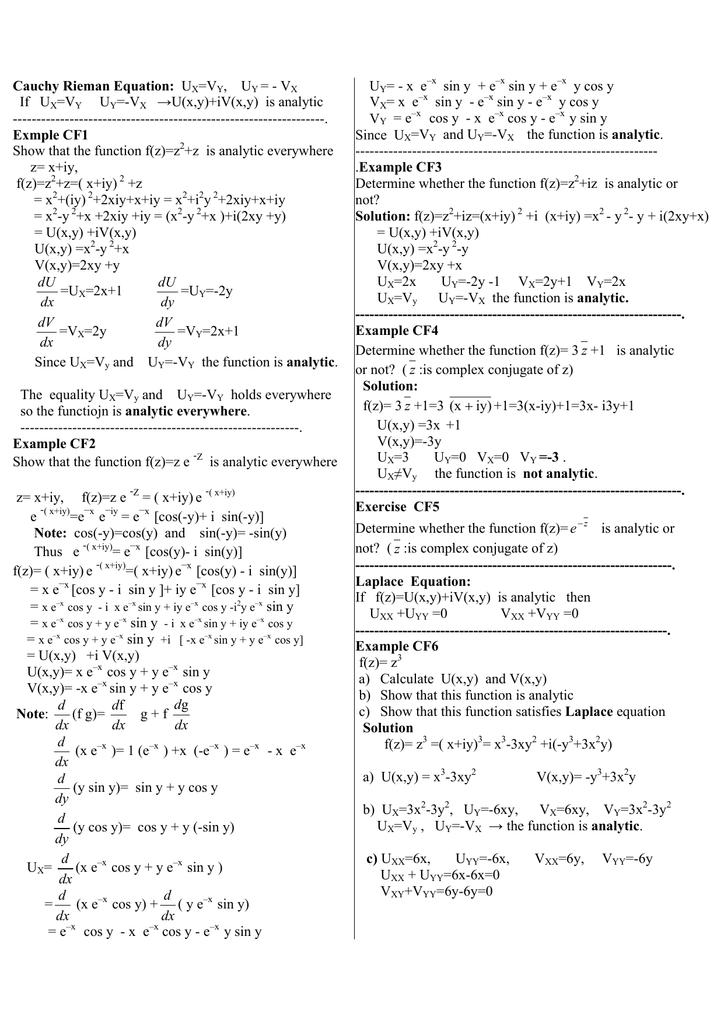
Ux Vy Uy Vx If Ux Vy Uy

Variablecomplejaysusaplicaciones 7maedicion Churchill Solucionario Co

Problem Set 10 Solution Random Variations Stochastic Systems Studocu

Automated Shape Differentiation In The Unified Form Language Springerlink

Pdf Partial Differential Equations Problem Sheet 1 Assem Elgazzar Academia Edu

Assignment 1 Solutions Maths8 Studocu

43 Solution 2
Frequenze Di Un Testo

Inferenza Causale Parte Iv Modelli Causali Strutturali

Solved 1 Draw The Tree Diagram For The Chainrule And Wr Chegg Com
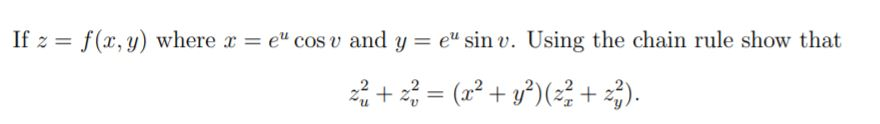
Solved If Z F X Y Where X Eu Cos V And Y E Sin V Chegg Com

Dizionario Culinario Lettera Z Nicola Cirelli Il Mio Mondo La Cucina

Nikon Z Fotocamere Fx E Dx Mirrorless

Solved Use Chain Rule O Find The Indicate Derivative Part Chegg Com
Solved Consider The Following F X Y Z Xe 5yz P 2 Chegg Com

Federica Eu Ricerca Operativa 1 Ottimizzazione Non Lineare Monodimensionale



